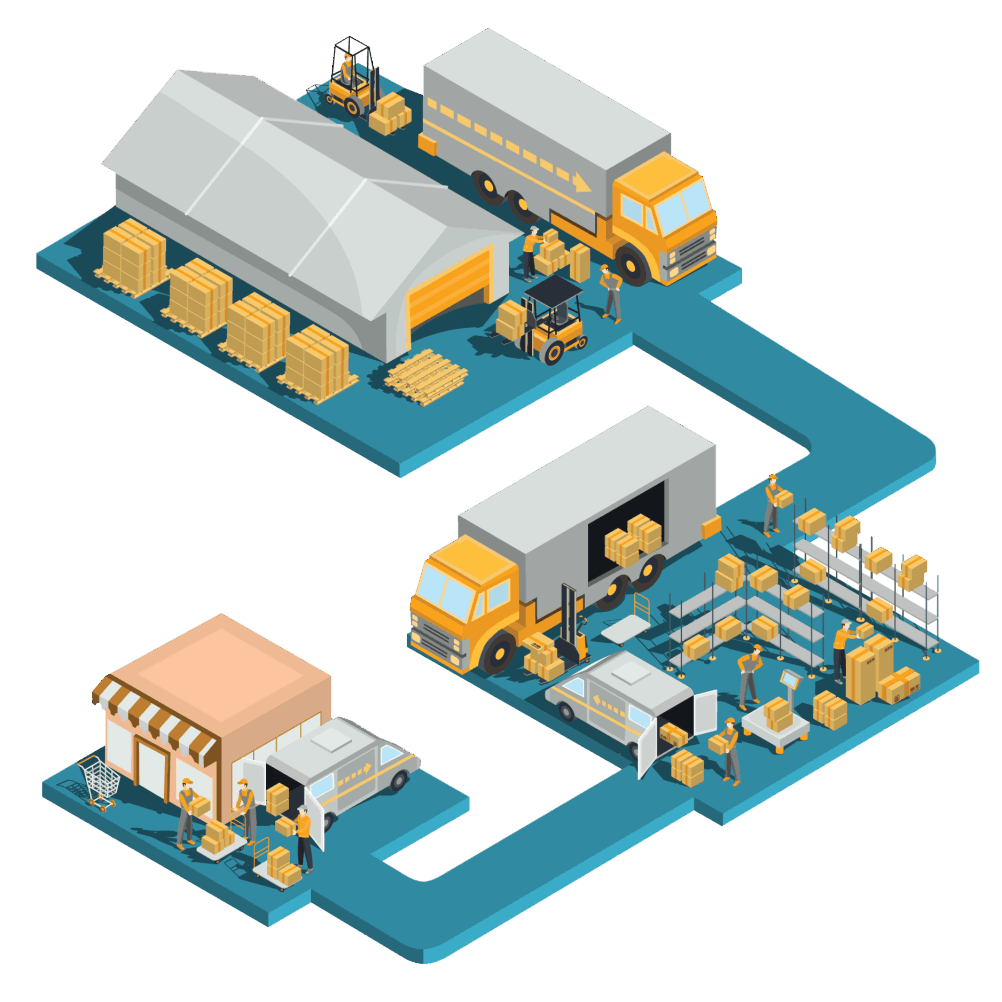
Why to focus on warehousing
1. Planning and management of material flow in terms of independence and interde- pendence of all elements in the production process.
2. Control of product distribution processes, from the planning of production vol- umes to the delivery of products to final customers.
3. Inventory Management to satisfy consumer needs.
4. Description of logistics inventory management processes, distribution of products and their integration into the overall system of processes going on in the company.
5. Analysis of logistics costs throughout the supply chain.
6. Development of logistics services.